Asymmetric Beam Patterns in Infrared LEDs: Smart Applications and Technical Advantages
Smart Applications and Technical Advantages
Principles and Advantages of Asymmetric Beam Design
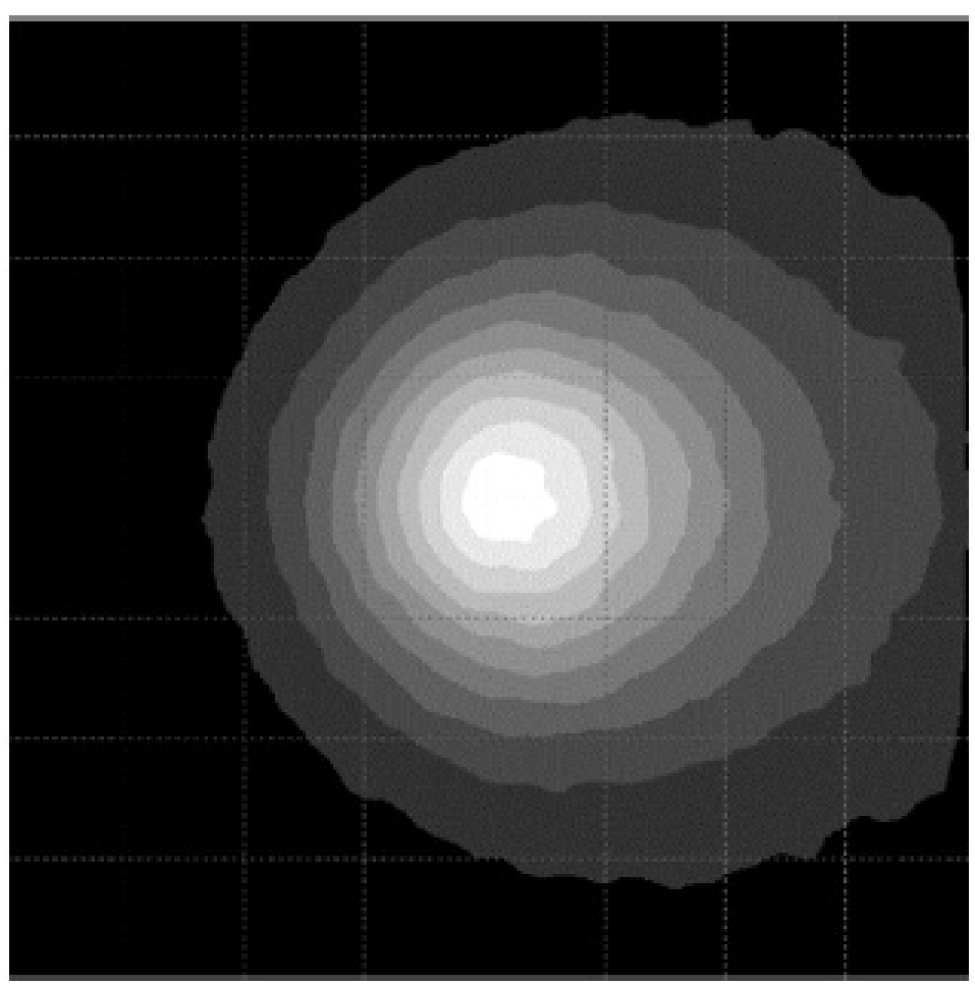
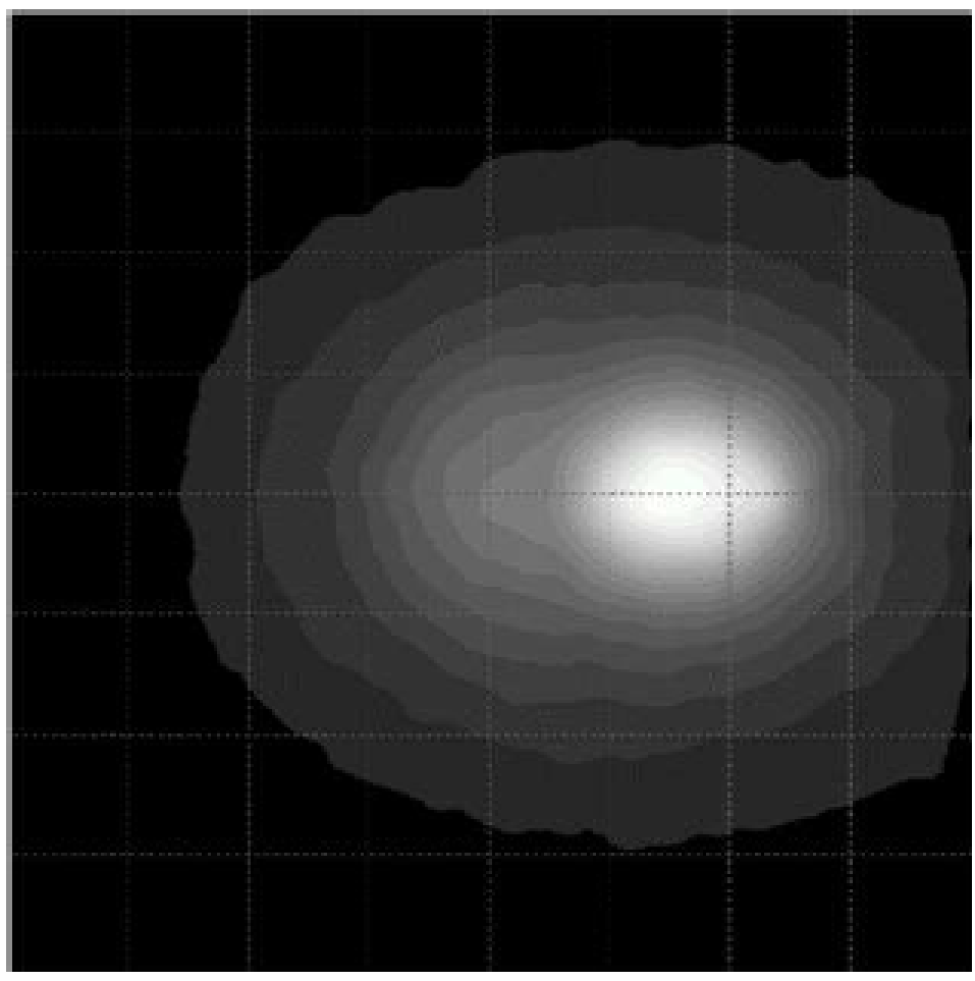
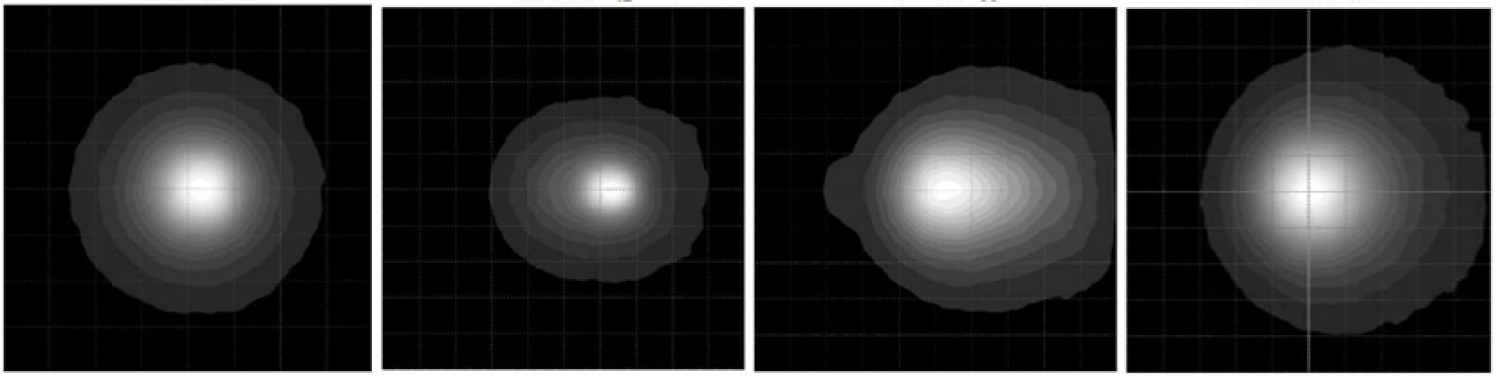
Traditional IR LED products typically feature symmetric beam patterns (such as circular or elliptical), with light intensity evenly decreasing around the central axis. However, in many real-world applications, this uniformity often leads to energy waste and suboptimal lighting efficiency. Asymmetric beam patterns are designed using sophisticated lens structures or packaging techniques to intentionally produce different beam angles along the horizontal and vertical axes.
Key advantages include:
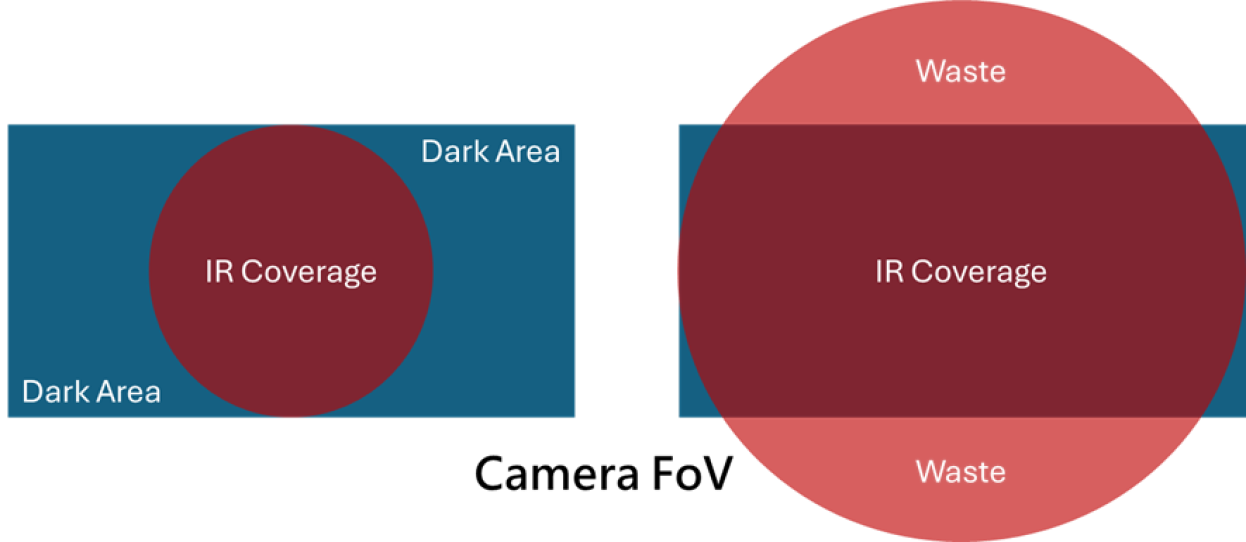
- Precise Field of View (FoV) Matching: Enables accurate projection of IR energy within the sensor or camera’s FoV, reducing ineffective illumination.
- Elimination of Hotspots and Shadows: Solves the issue of hotspots (over-bright zones) or edge shadows (dim areas) commonly seen in symmetrical beams at close range.
- Energy Saving and Efficiency Boost: Focuses the light on target areas, achieving higher effective irradiance with the same input power.
Application Scenarios
Asymmetric IR LEDs offer irreplaceable value in the following areas:

Smart Surveillance and Security Lighting

Iris/Facial Recognition and Access Control Systems

Automotive Sensing and Autonomous Driving

Virtual/Augmented Reality (VR/AR) Headsets
The asymmetric beam design in IR LEDs is a perfect example of “targeted engineering” in optoelectronics. It doesn’t merely pursue brightness, but rather smart light distribution. Beyond the applications mentioned above, could this concept also spark ideas for innovations in other fields?
Energy Focus have long been cultivating and growing our presence in the market. In fact, many of our products already utilize this advanced technology and are demonstrating their value commercially.
As the demand for sensor precision and energy efficiency continues to rise, asymmetric beam IR LEDs are poised to become the mainstream solution for future smart vision, security, and human-machine interaction systems.